A constantly progressive pathology that is characterized by thinning of the articular cartilage is called arthrosis. It is more commonly diagnosed in patients over 40 years of age. Pathology develops at a young age, for example, in athletes.
What is arthrosis of the knee joint
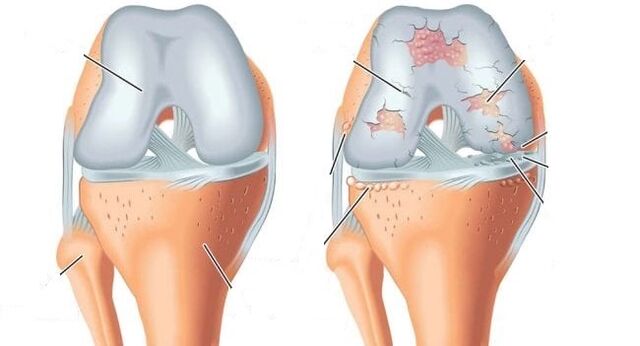
The disease is chronic, degenerative. Other names for knee arthrosis are gonarthrosis, deforming osteoarthritis. According to statistics, up to 22% of people in the world suffer from this ailment. Women suffer from it 2 times more often than men.
The reasons
Deforming arthrosis of the knee joint is a polyetiological ailment.
The primary form of the disease is provoked by increased loads on the knee area.
Secondary osteoarthritis is caused by systemic diseases. The main reasons that provoke disease of the knee joints:
- Sports activities. . . Intense training leads to thinning, wear and tear of cartilage tissue. Squats and running on hard surfaces are especially harmful to joints.
- Trauma. . . Meniscus injuries, dislocations or fractures often cause post-traumatic arthrosis.
- Obesity. . . The load on the knees increases. Excess weight contributes to joint wear and tear, meniscus injury.
- Metabolic disease. . . The joint tissues do not receive the required elements. Lack of vitamins and minerals over time worsens the condition of the cartilage tissue.
- Weak ligamentous apparatus. . . Due to the violation of the collagen structure, the joints are hypermobile. People with this diagnosis are prone to sprains, dislocations and microtrauma of the knees.
- Joint diseases. . . Often, osteoarthritis of the knee joint becomes a consequence of reactive, psoriatic or rheumatoid arthritis. With these ailments, cartilage tissue is destroyed.
Stages of the disease
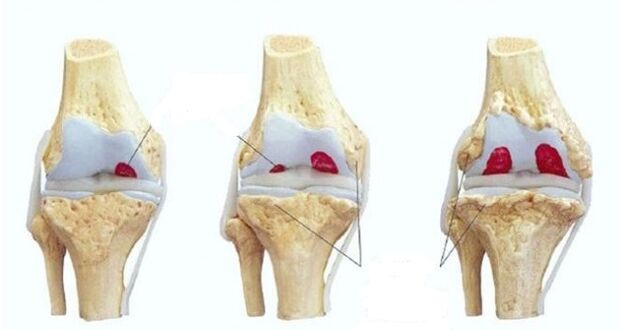
The medical classification includes 3 degrees of development of gonarthrosis:
- Stage 1there is no bone deformation. A characteristic symptom is recurrent pain (gonalgia) in the knee immediately after exercise. Sometimes there is a short swelling of the knee.
- Stage 2symptomatology increases. The pain is intense and long lasting, even with light exertion. During movement, a crunch is heard in the knee. The joint space narrows, thorns appear, synovitis develops (accumulation of exudate).
- Stage 3gonarthrosis has pronounced clinical manifestations. Due to the deformation of the joint, the patient's gait is disturbed, the mobility of the knee is limited. Sleep is disturbed from constant pain.
Knee arthrosis symptoms
Gonarthrosis does not occur suddenly. Symptoms have been increasing over the years. At first, painful sensations appear with strong loads, and over time, at rest. Symptoms of arthrosis of the knee joint:
- pain during prolonged sitting or standing;
- reaction to bad weather;
- discomfort in the knee after waking up;
- burning;
- loss of flexibility, knee stiffness;
- constant weakness of the lower extremities.
Why is the destruction of the cartilage of the knee joint dangerous?
The worst consequence of knee arthrosis is disability. Without timely treatment, the disease develops rapidly (hyperarthrosis, polyarthrosis) and leads to irreversible deformation of the joint. Other consequences of the disease:
- Infection. . . Pathogenic microorganisms enter the affected organ from other foci with the flow of lymph and blood or during diagnostic measures (arthroscopy, puncture). The multiplication of bacteria provokes an accelerated decay of cartilage tissue. Infection can lead to aseptic necrosis.
- Fractures. . . If the knee function is impaired, the load on the bones is uneven. Ligaments are weakened, which entails a high risk of fractures.
- Ankylosis. . . The disease is characterized by fusion at the site of the destroyed joint of 2 bones. The lower leg is fixed in a certain position, so movement is impossible.
Diagnostics
The main research method for gonarthrosis is radiography. In the photo you can see only hard tissue, the cartilage is invisible. Narrowing of the articular lumen indicates pathological processes. With little information content of the X-ray, the doctor prescribes other diagnostic methods:
- MRI. . . Helps to identify the earliest degenerative changes in cartilage.
- Knee ultrasound. . . Ultrasound examination allows you to assess the quality of the synovial fluid (lubricant) and its accumulation in the joint capsule.
- Scintigraphy. . . With the help of a contrast agent, it is easy to find the exact location of the cartilaginous tumor.
- General blood analysis. . . According to the results, the severity of the inflammatory process is assessed.
- Blood biochemistry. . . The presence and degree of damage to internal organs are determined by an increase in markers of inflammation.
- General urine analysis. . . It is performed to exclude inflammation of the urinary tract and kidneys.
How to treat arthrosis of the knee joint
To make a diagnosis, you can contact several specialists: therapist, traumatologist, rheumatologist, arthrologist, orthopedist. Treatment of gonarthrosis is complex. When prescribing a therapeutic regimen, the doctor takes into account the patient's age, the degree of the disease, and concomitant pathologies. Treatment of arthrosis of the knee joint is aimed at solving several problems at once:
- relief of pain;
- normalization of cartilage and bone tissue nutrition;
- improving the work of the muscles next to the affected joint;
- restoration of knee mobility.
Medicines
Depending on the type and stage of the disease, doctors prescribe different groups of drugs. Regardless of the type of gonarthrosis, the dosage of drugs and the duration of the course are selected by the doctor. Self-medication threatens the development of serious complications. The main groups and forms of drugs that are intended for the treatment of arthrosis of the knee:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. . . They relieve pain, reduce inflammation. NSAIDs are prescribed in the form of tablets, intramuscular injections, ointments for external use.
- Glucocorticosteroids. . . They are used for severe pain and severe inflammation. The drugs are potent, therefore they are prescribed when other means do not help.
- Chondroprotectors. . . They restore cartilage tissue, supply the joints with nutrients. The drugs are prescribed in the form of capsules, ointments, and injection solutions. The therapeutic effect is observed after long courses - from 3 months to 1 year.
- Antibiotics. . . Appointed if arthrosis is caused by bacteria or viruses. They are used in the form of tablets.
- Hyaluronic acid. . . It is prescribed in the form of injections to replenish the volume of synovial fluid in case of its deficiency.
- B vitamins. . . Necessary for the restoration of nerve conduction in the joint. They are used in the form of injections.
- Immunosuppressants, cytostatics. . . They are prescribed if the disease develops against the background of disorders of the immune system. Most often used in tablet form
Pills
The basis of drug treatment is analgesic drugs. The most effective pills for arthrosis of the knee joint will be prescribed by a specialist.
Preparations for intra-articular injections
An integral part of drug therapy for arthrosis is the introduction of drugs into the joint cavity. Injections quickly relieve pain, stop disease progression, and help avoid or delay surgery.
Ointments for the destruction of the cartilage of the knee joint
The advantage of topical preparations is ease of use. The ointment penetrates the skin, reduces spasms, pain, inflammation. Due to their lower effectiveness, topical preparations cannot be considered as a complete substitute for injections or pills.
Diet therapy
There is no special diet for knee arthrosis. The patient needs nutritional correction to eliminate metabolic disorders, strengthen immunity, and reduce inflammation. Basic dietary requirements:
- eat a balanced diet, include vegetables, herbs, fruits in the menu;
- spend 1-2 times a week fasting days: fruit, vegetable, kefir, curd;
- exclude dishes that contain smoked meats, fatty meats, refractory fats, saturated fish, meat broths;
- limit salt intake to 5 g / day;
- drink at least 2–2. 5 liters of water daily;
- include in the diet lean meat (chicken, veal), fish, seafood, whole grain bread, dairy products, cereals, unsalted cheese, low-fat cottage cheese.
Physiotherapy for gonarthrosis
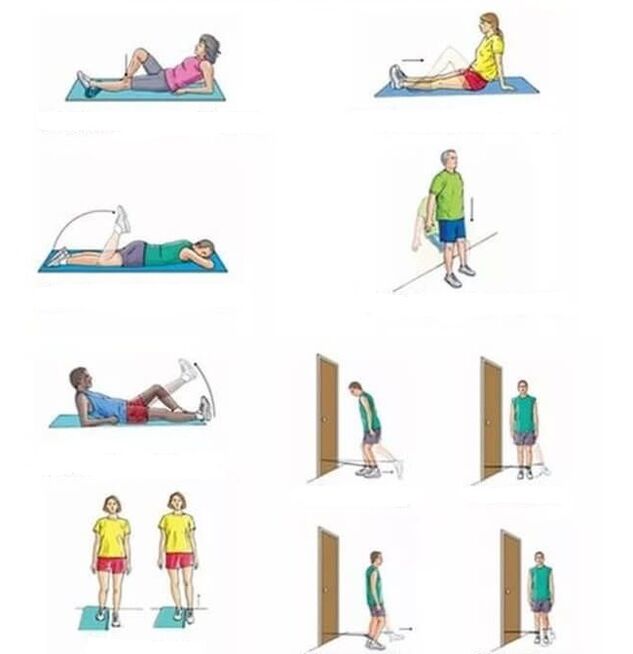
Exercise therapy helps to reduce pain during inflammation, improve joint mobility, and prevents osteoporosis. Therapeutic workouts are carried out every day for 10-15 minutes. Gymnastics for arthrosis of the knee:
- In a sitting position with a straight back, slowly straighten your leg at the sore knee, hold for 3 seconds, then lower it. Repeat the exercise 4-6 times.
- Stand near the table, lean on your buttocks. Bend your knees slightly, spread your feet to the sides. Lean forward with your back straight, then come back. Make 5-7 bends.
Manual therapy
At the initial stage of the disease, minimally invasive techniques help to stop degenerative processes in the joint. During manual therapy, the patient's muscles and joints are stretched, nerve fibers are relaxed, and seals are rubbed. The objectives of the methodology:
- provide blood flow to the damaged area;
- facilitate the patient's well-being;
- reduce the intensity of symptoms;
- restore the motor functions of the knee.
Physiotherapy
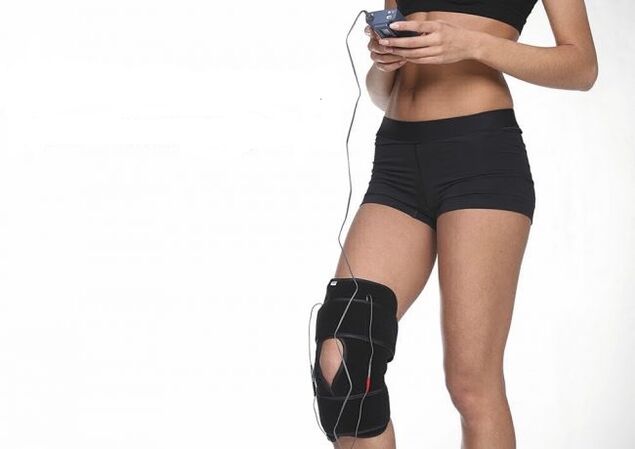

In order to prevent exacerbations of chronic arthrosis of the knee, the patient is prescribed physiotherapy. Types of procedures for gonarthrosis:
- Acupuncture. . . The sessions are conducted by a specialist who acts with needles on biologically active points. With the help of acupuncture, it is possible to stop pain, relax muscle tissue, and relieve swelling.
- Ozone therapy. . . Intra-articular injections of ozone increase the motor activity of the damaged joint. The effect appears after 3-5 treatments.
- DENAS-therapy. . . The method is based on the use of energy-informational impulses. DENAS device is a wearable electrostimulator that can be used at home. It has anesthetic, decongestant, antiallergic effect on the affected area.
Knee arthrosis surgery
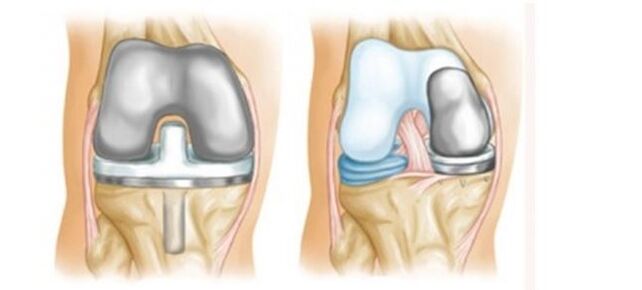
Surgical treatment is prescribed at the last stage of arthrosis, when other methods of treatment have failed. The following types of operations are applied:
- Arthroscopic arthrolysis. . . The joint cavity is opened and the fibrous tissues are excised. Used to relieve pain and partially restore knee functionality.
- Arthroplasty. . . The deformed joint is removed in whole or in part. An artificial device is placed in the vacant space that simulates a healthy femoral-patellar or femoral-tibial joint.
- Endoprosthetics. . . The destroyed joint is replaced with an implant.
Folk remedies
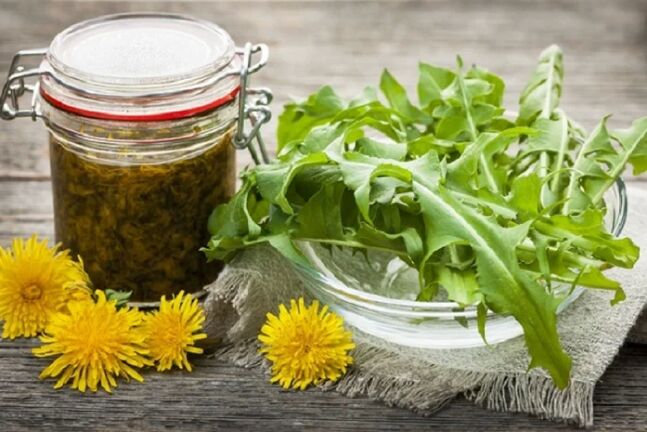

At home, treatment should be carried out in consultation with the attending physician. Traditional methods of therapy (compresses, massages) relieve the inflammatory process, eliminate pain. Treatment is aimed at improving intra-articular circulation. Effective traditional medicine recipes:
- Dandelion tincture. . . Pour the washed plant roots (50 g) with vodka (0. 5 l). Place the container in a dark place for 2 weeks, shake occasionally. After this time, massage the sore knee with tincture daily at night until the entire volume is consumed. A compress with medicine can be used to warm a chilled knee (apply at night).
- Celandine. . . Saturate the cloth with freshly harvested plant sap. Apply to the sore knee, wrap with a woolen scarf on top, hold for 1 hour. For better absorption, pre-coat the knee with vegetable oil. The duration of therapy is 7 days, then take a break for 10 days, repeat the weekly course.
- Decoction of nettle and burdock. . . Pour boiling water (400 ml) dried and mixed in an equal amount of plants (2 tbsp. L. ). They need to be insisted on a water bath for 15 minutes. Cool, strain. Drink 200 ml 2 times a day 20 minutes before meals for 10 days.
New in the treatment of arthrosis of the knee joint
Doctors offer a replacement for expensive operations - stem therapy. The new technique helps to restore cartilage, reduce pain, and restore mobility to the knee.
For treatment, undifferentiated cells are used, which are taken from the patient's bone marrow by puncture.
Joint transplantation is performed by injection or surgery. The number of injections varies from 1 to 3, depending on the severity of the disease.
Prevention of joint diseases
To avoid degenerative changes in the knee joint, it is necessary to reduce the load on it. Basic preventive measures:
- maintain a normal body weight;
- in case of forced loads, fix the knee with an elastic bandage;
- eat a balanced diet;
- train the muscles of the lower extremities;
- rule out knee injuries;
- treat inflammatory processes in the body in a timely manner.